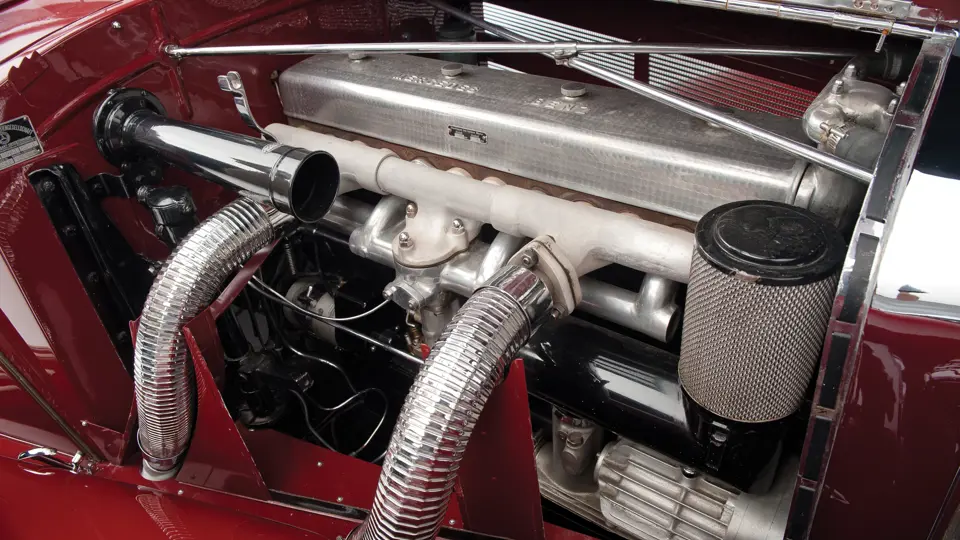
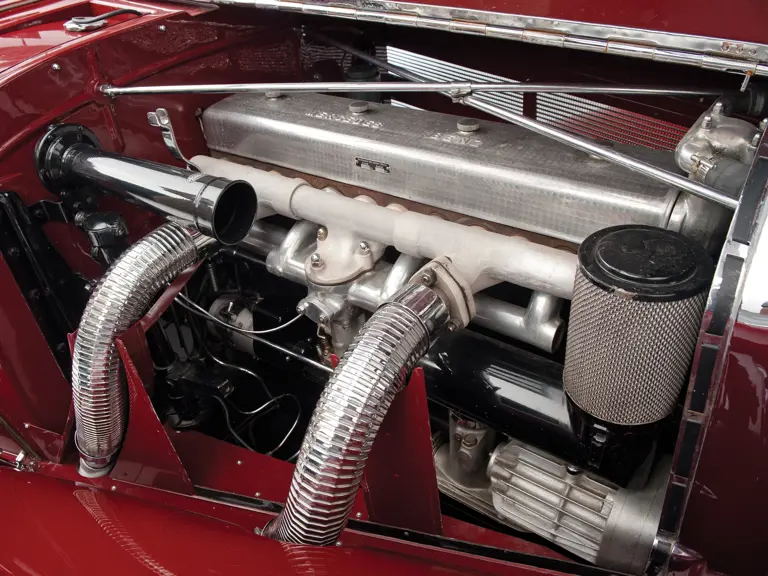
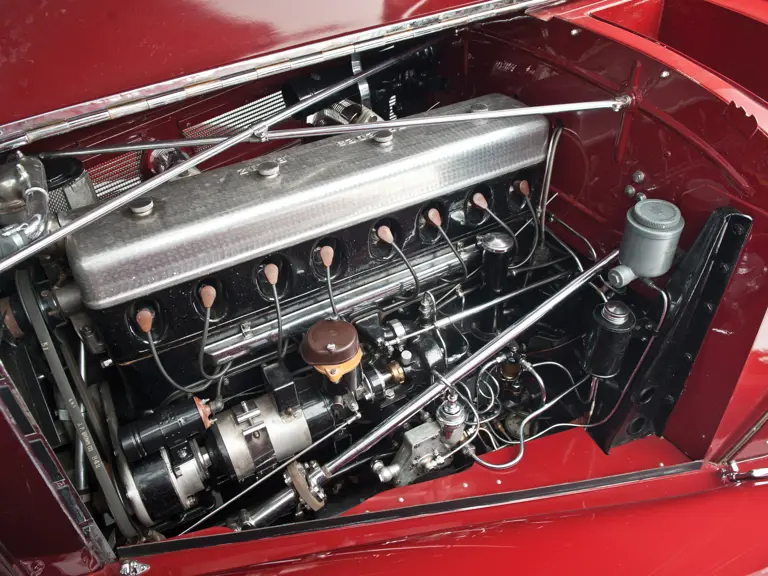
115/180 hp, 5,401 cc supercharged overhead valve inline eight-cylinder engine, four-speed manual transmission, four-wheel hydraulic drum brakes, independent coil spring front and rear suspension. Wheelbase: 129.5"
- Offered from the Lyon Family Collection
- Single-family ownership for two decades
- The 1936 Paris Salon car
- Complete with copy of original build sheet; delivered new to Jean-Claude Solvay of Belgium
- Inspected in person by experts from Mercedes-Benz Classic Germany
- Matching-numbers
- One of a limited few 540 Ks with coupe coachwork
The abundant power, stiff, rugged frame and supple fully-independent suspension made Mercedes-Benz’s supercharged 540 K suitable for a vast array of coachwork. Sindelfingen was more than capable of building anything and doing so in the finest materials and to the highest standards of fit, finish, function and luxury in the world.
Yet despite Sindelfingen’s designers’ demonstrated ability to create exceptionally beautiful closed cars, the vast majority of Mercedes-Benz 540 Ks were fitted with open bodies in one of the several styles of Cabriolets. Most of those were four-seat Cabriolet Bs with blind rear quarters. Surprisingly, only a precious few 540 Ks – just 42 in four years’ production – received closed coachwork.
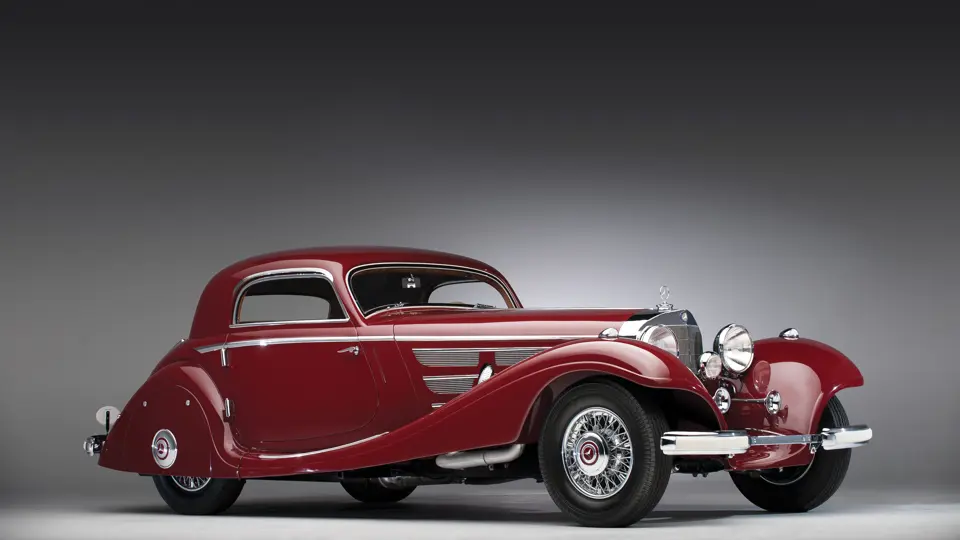
Only about seven of those were coupes, making them exceptionally rare examples of Sindelfingen’s creativity and style. One of the foremost examples is this 1935 Mercedes-Benz 540 K, the car Mercedes-Benz chose for its 1935 display at the important Paris Salon to show the quality and beauty of its premier product.
Sindelfingen
Daimler-Benz concentrated automobile coachwork production at Sindelfingen, a massive facility that had developed a combination of medium volume production methods for high quality coachwork and a select group of designers and craftsmen who conceived, created and built low volume, nearly custom, bodies for the finest chassis in the Mercedes-Benz line and crafted a few highly specialized bodies for the most demanding clients.
Sindelfingen had been constructed during the First World War to build aircraft. The Treaty of Versailles ending the war prohibited aircraft construction in Germany on the industrial scale for which Sindelfingen had been constructed and equipped, so Hanns Klemm, the factory’s manager, eventually reorganized the factory to build automobile, truck and bus bodies. Sindelfingen continued to employ classic coachwork construction techniques with wood frameworks and sheet metal panels throughout its history, but Mercedes-Benz also added high capacity steel presses of 750- and even 1,000-tons to stamp out large, complex panels, particularly fenders.
Sindelfingen’s aircraft-building history manifested itself in a facility-wide devotion to quality that remained central to its operation throughout the Thirties. Specialized tools, fixtures and machines were designed and built in its own shops. Processes were meticulously planned and documented. A strict quality-control system inspected every body, whether it was for a modest 170 H or an elegant “Großer Mercedes” 770 Pullman-Limousine.
Klemm was succeeded by Josef Bildstein, who later took over Daimler-Benz’s Mannheim factory and turned over management of Sindelfingen to Wilhelm Haspel under whose leadership the factory became a major success for Daimler-Benz. It was a complicated undertaking in which every aspect of coachbuilding was integrated, from selecting and drying the beech and ash used for framing through stamping and forming metal panels to final assembly and painting. And Sindelfingen did every kind of bodywork, from one-off and low-production bodies for the 500 K, 540 K and Großer Mercedes to volume production of Mannheim’s 170H and V, truck cabs, specialized truck bodies, buses and even contract work in volume for BMW and Wanderer. Haspel’s success at coordinating this diverse facility was evident in his later promotion to Daimler-Benz managing director in 1942.
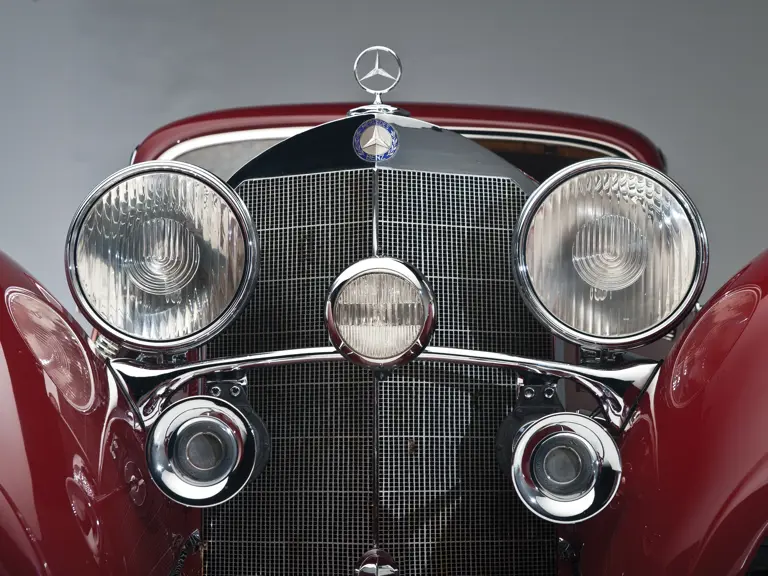
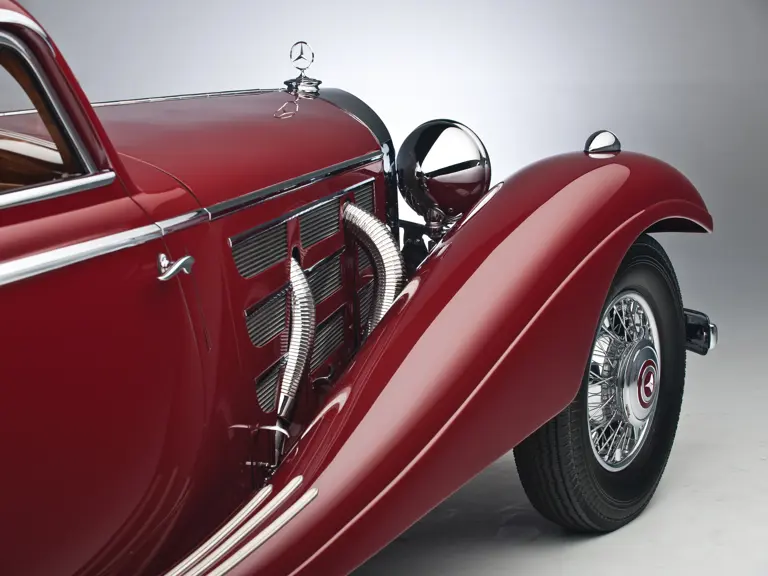
In September 1932 Hermann Ahrens joined Mercedes-Benz from Horch to head the Sonderwagen (special vehicles) section, designing and building limited production coachwork for the top Mercedes-Benz models. Ahrens would design and oversee construction of all limited-production Mercedes-Benz coachwork for nearly 40 years, including the great sports roadsters and coupes on the eight-cylinder supercharged chassis. It is his artistry that created the magnificent sweeping partially-skirted fenders, integrated running boards and deftly-shaped passenger compartments and doors that so effectively complemented the imposing long hoods and exterior exhaust pipes of the supercharged 500 K and 540 K.
Mercedes-Benz produced almost all the coachwork for even the most expensive and luxurious of its automobiles. According to the research of Jan Melin, just 89 of the 928 380, 500 K and 540 K chassis built were supplied to outside coachbuilders. That is just 9.6%, a tiny portion of the total production and largely unprecedented among luxury automobile manufacturers in the Thirties.
The combination of superb engineering, high quality materials, meticulous quality control and inspired design of the supercharged eight-cylinder Mercedes-Benzes with the limited-production coachwork of Sindelfingen brought into existence some of the finest and most respected automobiles of all time.
Enthusiast magazines of the time were unremitting in their praise. One described the 500 K with these words: “[T]his is a master car for the very few. The sheer insolence of its great power affords an experience on its own. The design and construction throughout are typically thorough and well-executed.” Of the 540 K another said: “As a piece of engineering, it stands unsurpassed. It is amongst the most luxurious, as well as the fastest, touring cars in the world.”
S/n 130944
With so few of the 540 Ks bodied as coupes, the selection of this car to represent Mercedes-Benz at the important Paris Auto Salon in October 1936 was unusual. Yet, upon consideration, it is completely appropriate and even sensible. Indeed, according to the Mercedes-Benz archives’ delivery papers and internal documents, the car is referred to as a “Spezial Coupe.”
Paris was then the center of art, design, literature, style and society in Europe. The aerodynamic revolution in automobile design was then at its inception and was practiced eloquently by French coachbuilders, whose combination of Machine Design principles, Art Deco embellishment and aerodynamic refinement was the center of attention. The 1936 Paris Auto Show brought some of the most imaginative designs, like Marcel Letourneur’s Aerosport coupe on the Delage D8 120 chassis and Jean Bugatti’s Type 57 Atalante, to the public’s eye. This Mercedes-Benz 540 K Coupe was more than competitive with the French salon’s best.
Prior Mercedes-Benz coupes had included one for the Mercedes-Benz “Silver Arrows” team driver Rudi Caracciola, an eminently practical automobile for a driver who needed to criss-cross Europe in all weather conditions to race the W 25 model GP car. In 1934 Wilhelm Haspel had suggested the Autobahn-Kurier, a fastback five-window design with teardrop fenders of which two were built on each of the 500 K and 540 K chassis. Hermann Ahrens’ Sonderwagen facility completed the first Autobahn-Kurier in only ten weeks in order to make its auto show debut, an example of the shop’s ability to create a completely new and dramatically different design on an abbreviated schedule.
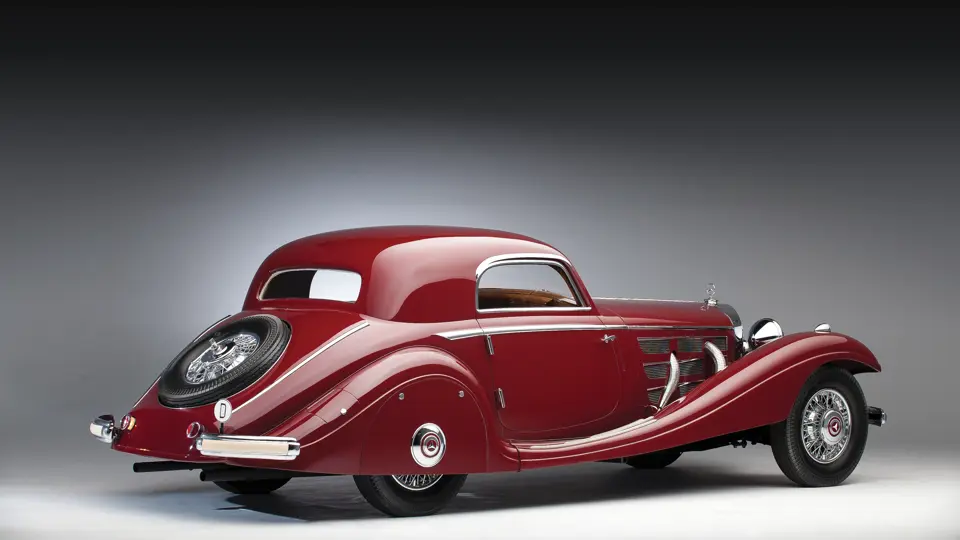
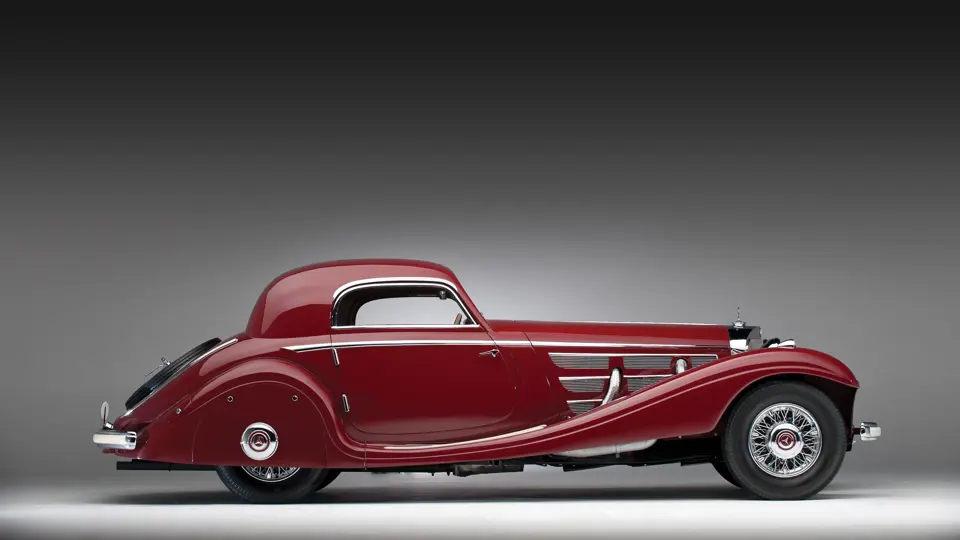
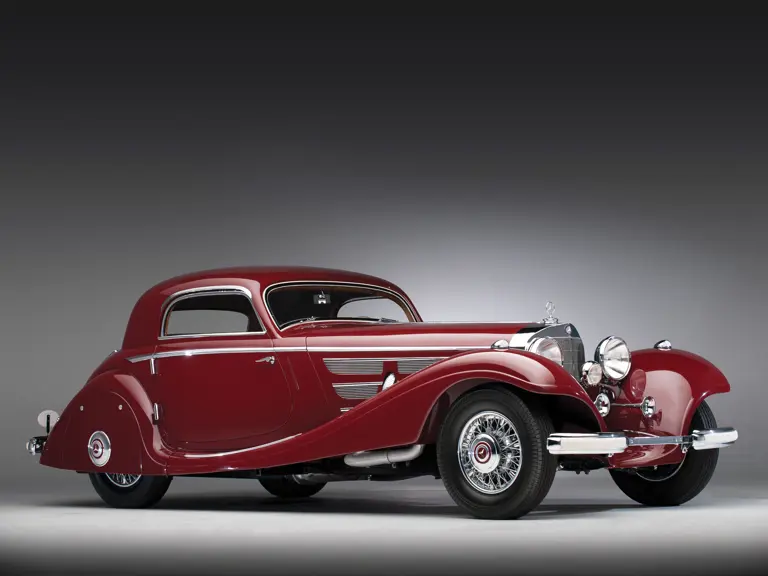
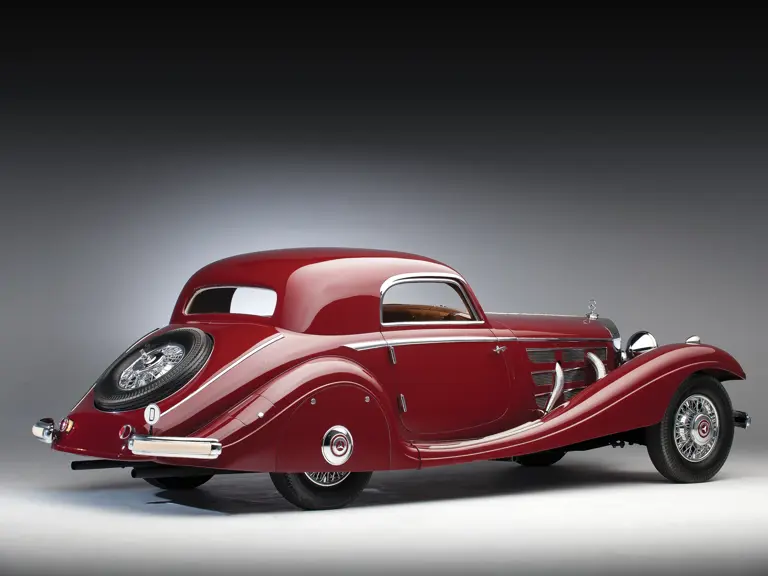
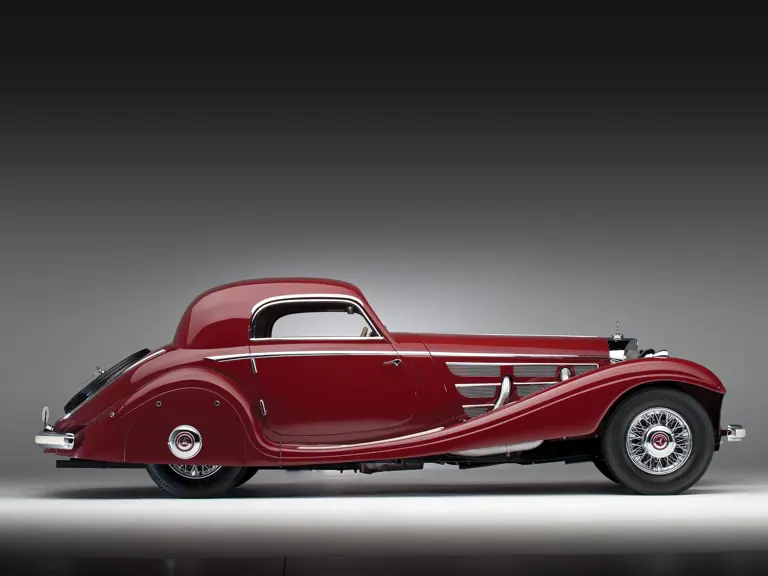
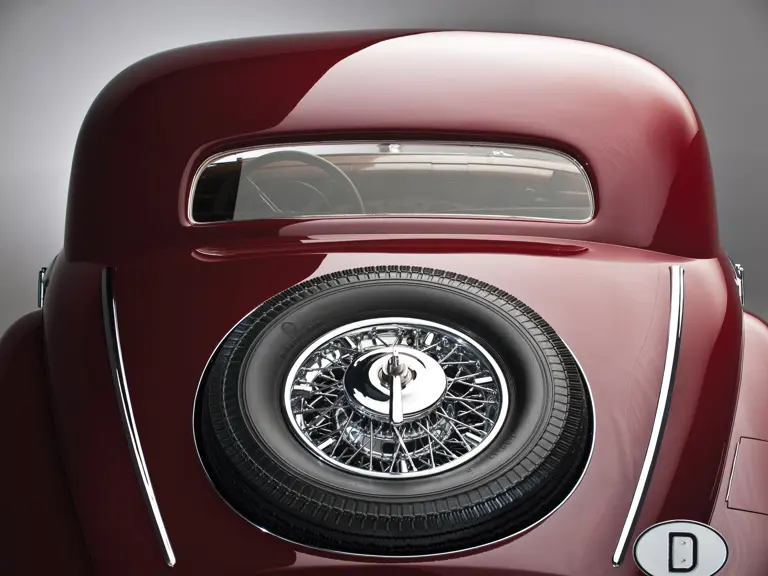
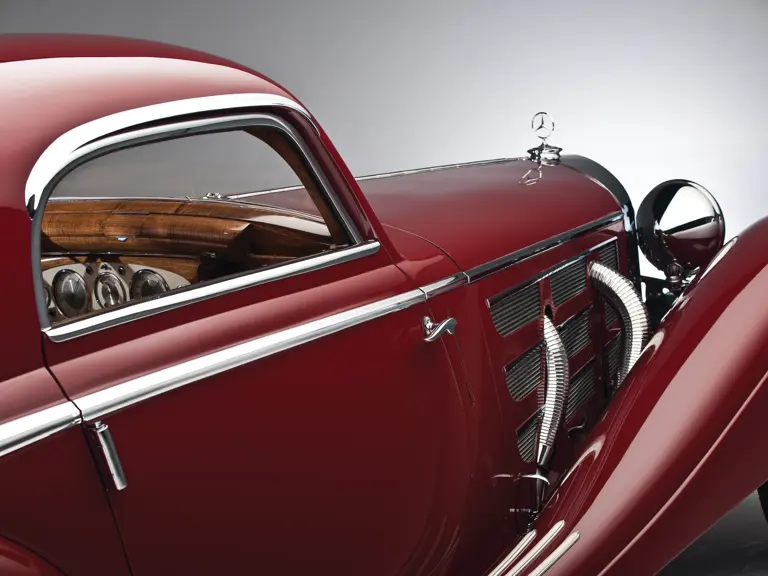
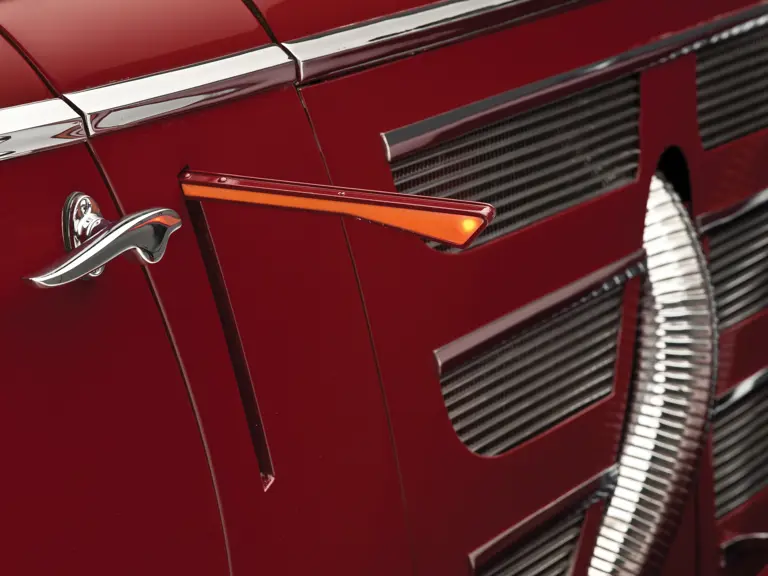
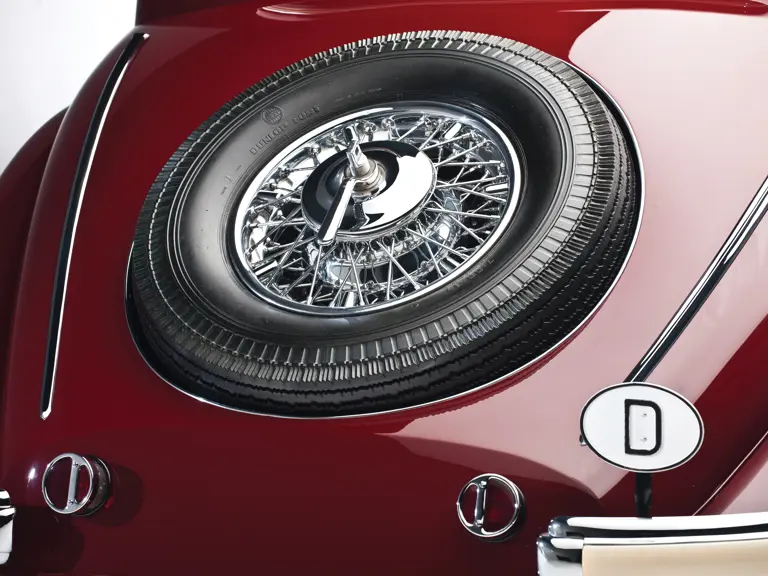
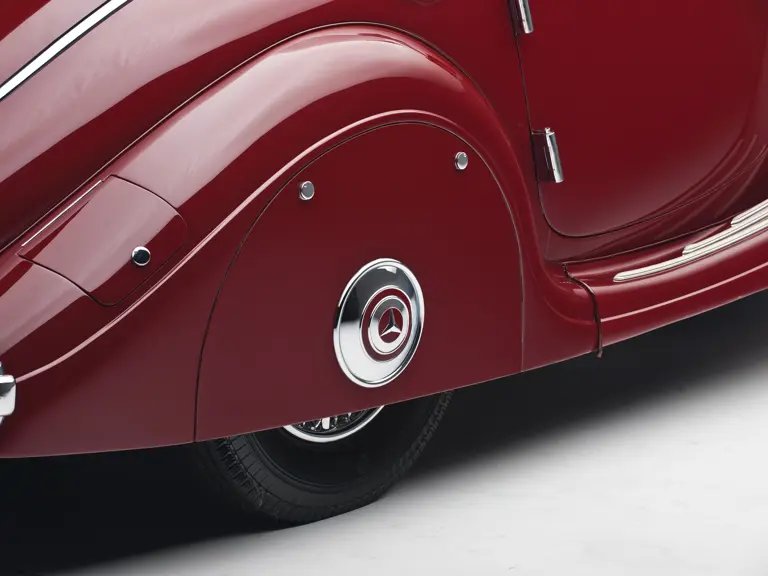
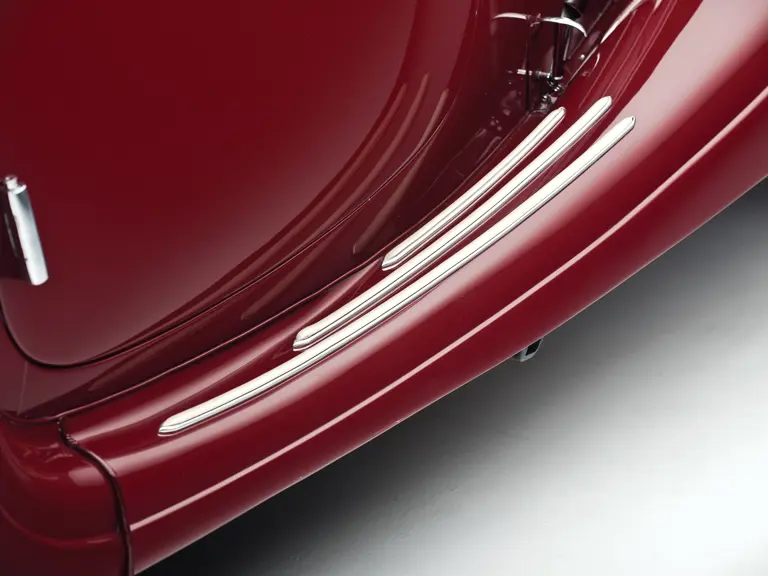
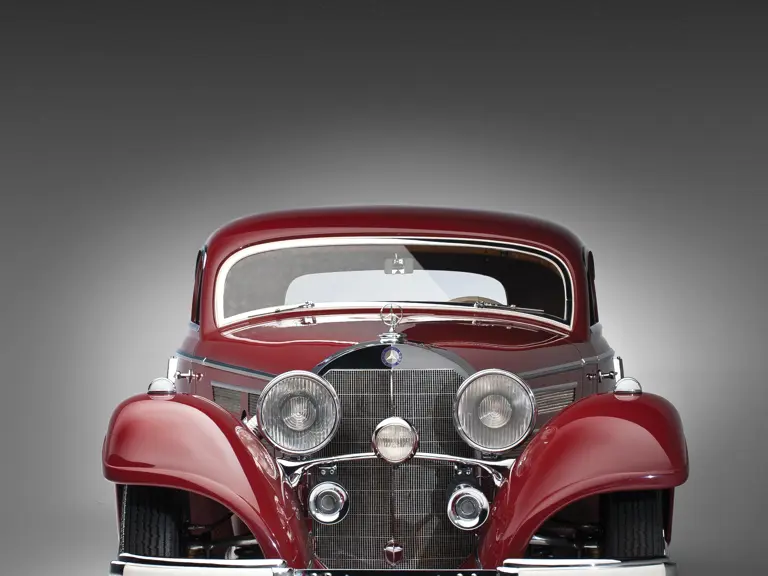
The Paris show coupe is another example of the creativity and masterful execution of which Sindelfingen was capable. Its sweeping front fenders merge into small running boards, then curve upwards into teardrop-flared rear fenders. The rear wheels are skirted, with a chrome emblem repeating the look of the front wheel’s centerlock hub. A tasteful chrome beltline molding accents the break of the hood side and extends back across the door to end near the top of the rear fender where its termination parallels the curve of the fender top. The roofline is rounded at the rear but merges nicely with the tapering rear deck, which contains a stacked pair of spare wheels and tires set nearly flush with the deck surface.
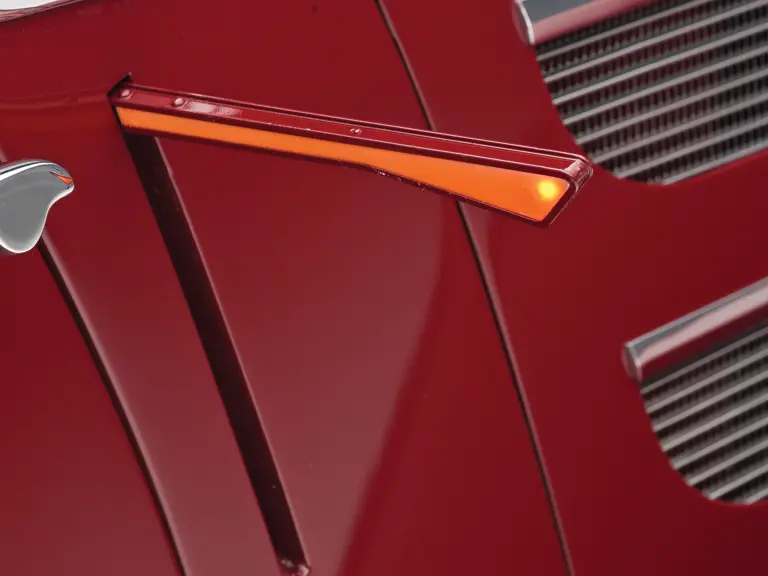
An attractive styling feature is the swage line which accents the sides of the fenders. It parallels the fender tops from the front valence the full length of the car, curving up and around the rear wheel skirts then down across the full width of the rear valence. The effect draws attention, visually reducing the fenders’ tall profiles.
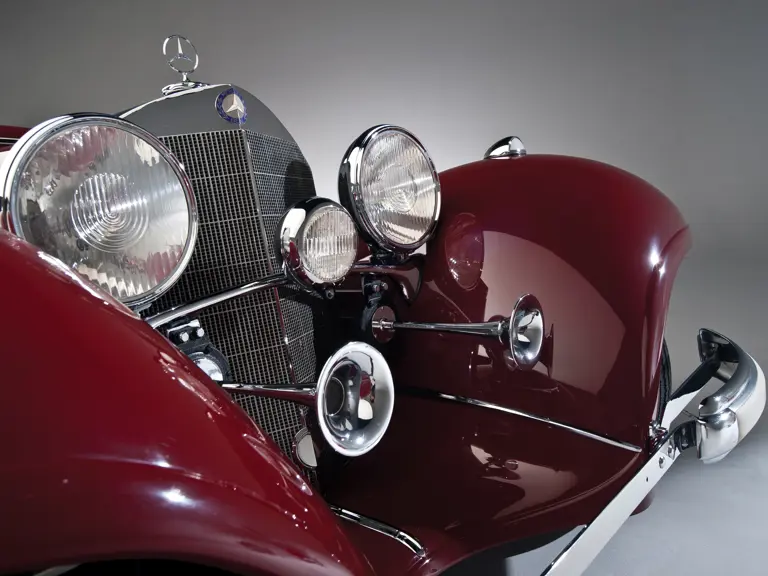
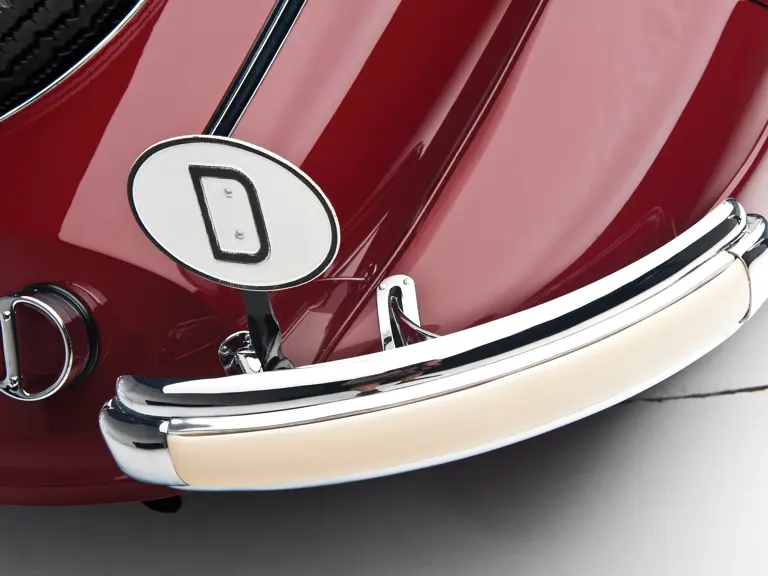
Bosch headlights in chrome nacelles nestle between the fenders and the gently raked vee radiator. A single small fog light is directly in front of the radiator, and a pair of long chrome horn trumpets also sit between the fenders above a split chrome bumper which is repeated at the rear.
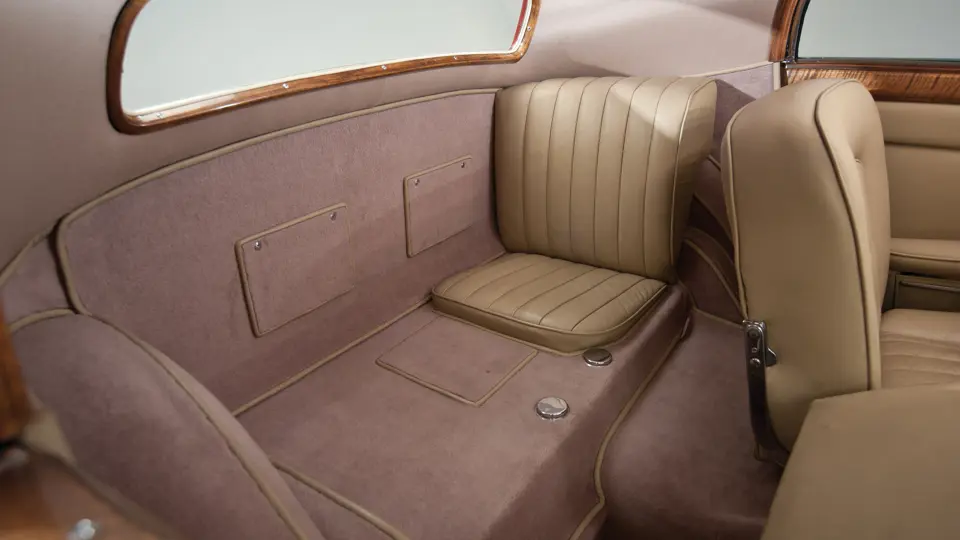
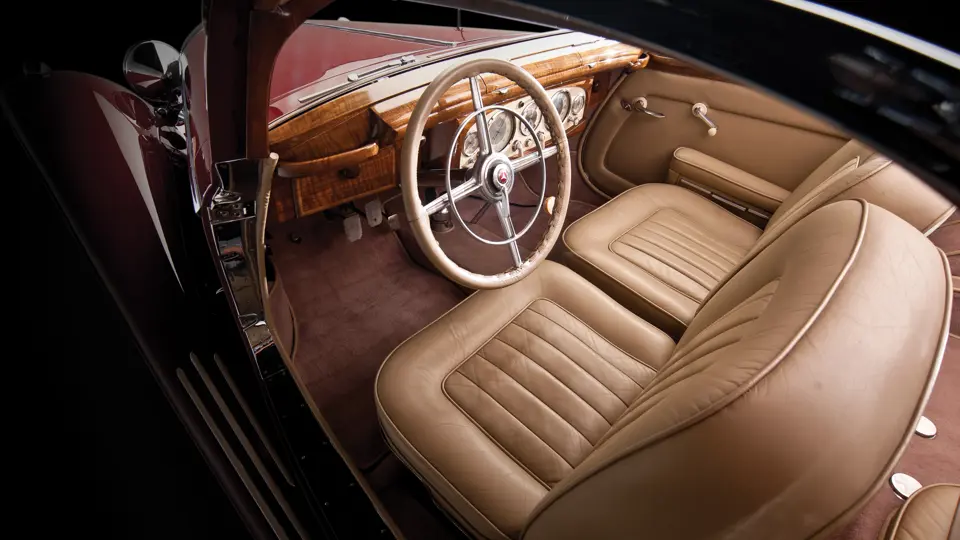
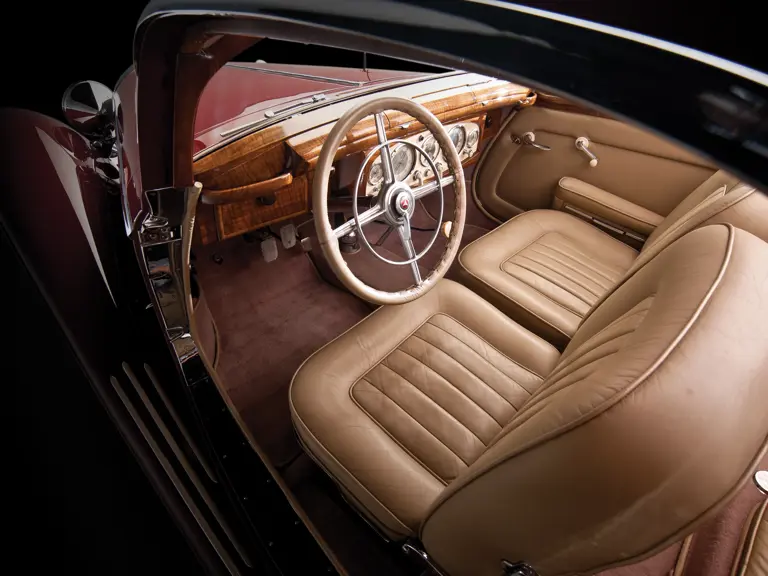
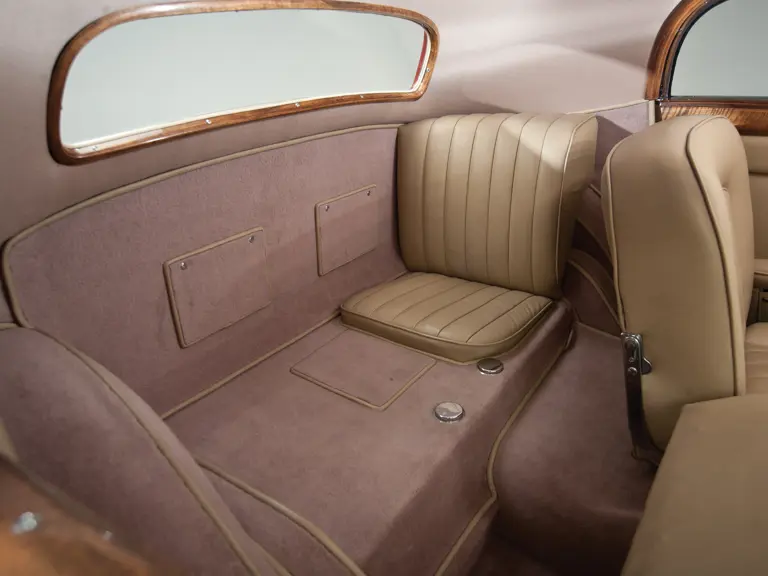
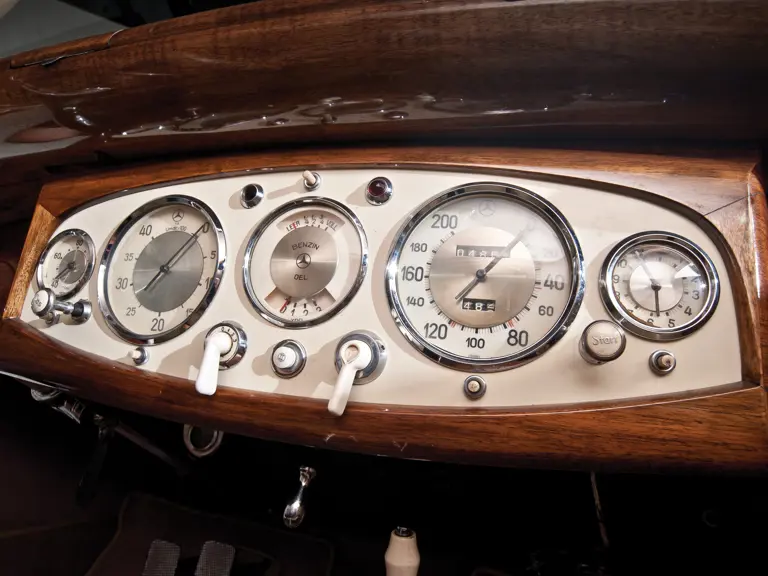
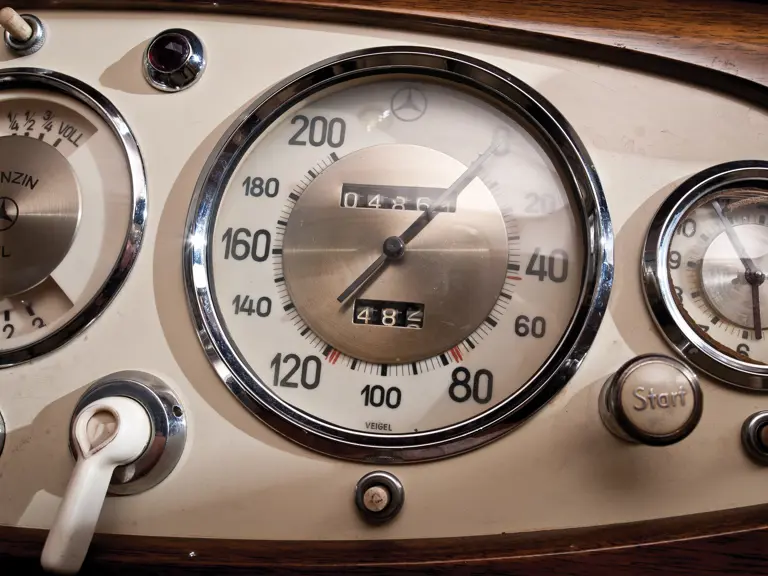
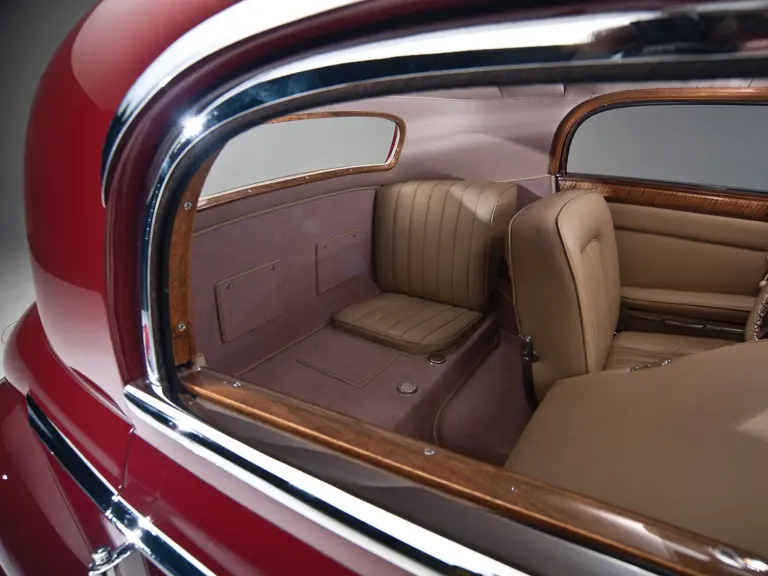
The interior is invitingly upholstered in tan leather with a plain white instrument panel in the highly finished wood dashboard. The steering wheel is leather covered. A transverse rear seat accommodates one passenger, in addition to the two in the front, or makes room for luggage.
After being displayed in Paris, the 540 K Coupe was first returned to Sindelfingen and then in December delivered to Jean-Claude Solvay of the Belgian chemical company dynasty in Belgium. Subsequently it became part of the collection of American Connie Bouchard in the 1960s, who undertook its restoration before selling it to John Mozart. It then was acquired by the Imperial Palace Collection from whom the Lyon family acquired it in the late 1990s. Since then, it has remained in the Lyon Collection, always treated to professional maintenance and climate-controlled storage.
Inspection
In preparation for the car’s offering in Monterey this August, this car was inspected in person by two veteran experts from Mercedes-Benz Classic Germany. Their findings were very positive. In their expert opinion, they concluded that although the car had been restored, it retained a great deal of originality in its components. The engine is matching numbers (130944) and retains its original number plate. In fact, they believe the body has never been off the car and the rear axle itself never removed – testament to the car’s originality. The transmission is original to the car, and it was determined that the steering is of the correct series. Minor modern improvements were made, including modern telescopic shocks, but the workmanship was professional and well done in their estimation. Again, the overall impression imparted on these Mercedes experts was very favorable.
Its deep red livery dramatically accents the sweeping lines of Hermann Ahrens’ dramatic coupe coachwork. One of only about seven coupes built on the Mercedes-Benz 540 K chassis, its effect today is, if anything, even more dramatic than it was at the Paris Salon of 1936.
It is the perfect complement to Ahrens’ high door, long tail Spezial Roadster, a vivid example of Mercedes-Benz’s mastery of power, speed, handling, comfort and design at the height of the golden age of classic automobiles.




































 | Monterey, California
| Monterey, California